Microsoft Windows exercises more restricted security control when connecting to a WebDAV server over HTTPS. The server must have a valid SSL certificate for its domain name or IP. Further configuration is needed if the certificate is self-signed; otherwise, the connection fails with suspicious error messages.
In our example, the WebDAV service runs on IP 192.168.56.2 and uses a self-signed certificate (for example, one generated through the SSL Certificate Creation Wizard in TSRMC). Steps 1 and 2 can be skipped if an SSL certificate file is already present.
1. Access the WebDAV URL
Access the following URL in your browser to initiate the connection:
https://192.168.56.2
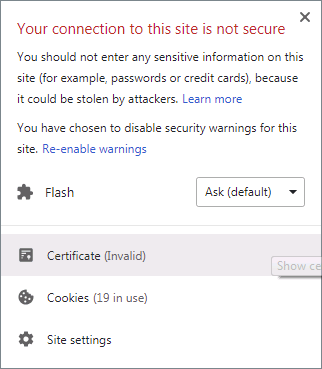
2. Export the Self-Signed Certificate
Click on the 'Site Information' icon in the browser's address bar and open the certificate information dialog. Export the certificate to a local file (e.g., 192.168.56.2.crt). If you are using Internet Explorer, you might need to run it as an administrator to export the certificate.
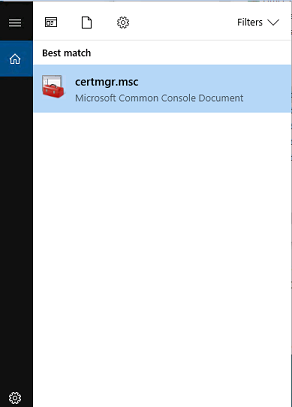
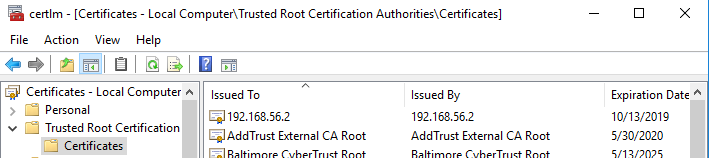
3. Launch Certificate Manager
Click the Windows Start button and search for the program certmgr.msc.
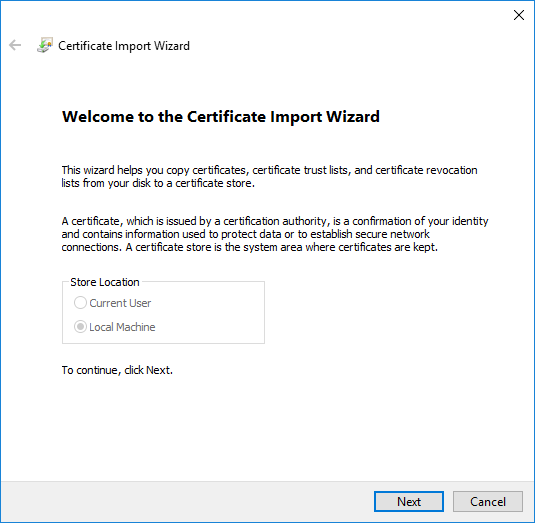
4. Import the Certificate
Right-click Certificates -> Trusted Root Certification Authorities, and select All Tasks -> Import to bring up the Certificate Import Wizard. Use the Browse button to select the exported certificate file, and click Next.
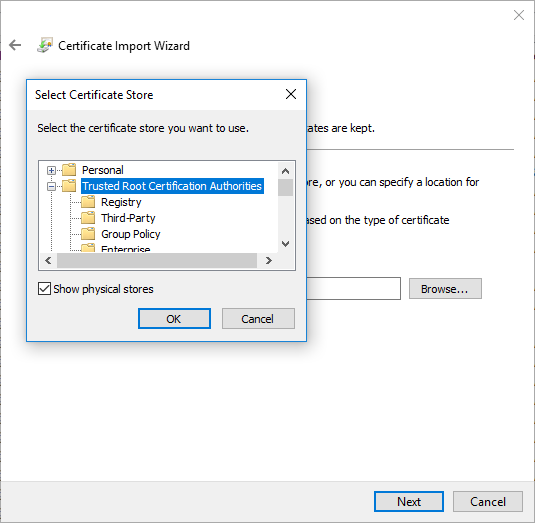
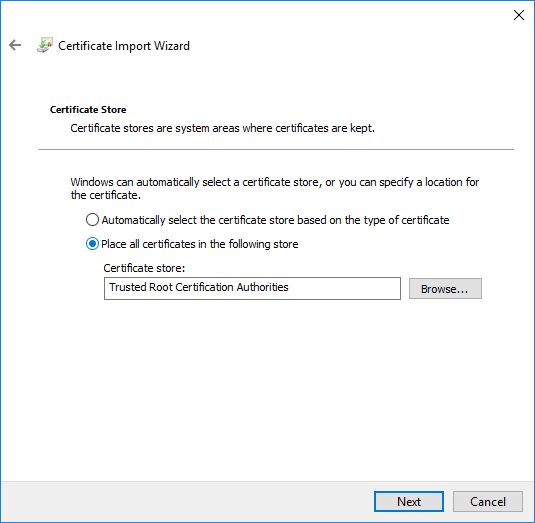
5. Select the Trusted Store
Select Place all Certificates in the following Store. Click Browse, check the option Show Physical Stores, expand the tree, and select Trusted Root Certification Authorities -> Local Computer. Then click OK and Finish.
The self-signed certificate has now been imported. You might need to re-launch certmgr.msc to verify the installation.
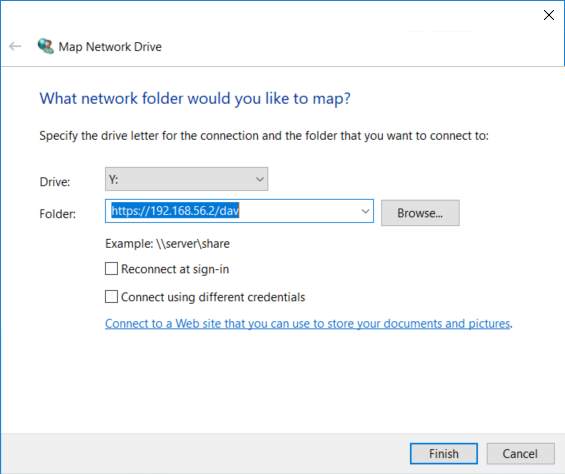
6. Map WebDAV as a Network Drive
Now that the certificate is trusted, you can map the WebDAV path as a network drive in Windows Explorer.